25 ++ yield point force extension graph 319625-Yield point force extension graph
⇒ This graph shows a stressstrain graph for copper It looks like the forceextension graph shown earlier, but this graph will be valid for ANY sample of copper ⇒ OP on the graph represents the range of tensile stree for which the copper obeys Hooke's law The gradient of this section is the Young modulus for copper· yield point · · The area under a Force –extension graph or To plot a graph like this, measurements of extension need to be taken when adding weights to a material and when removing them After plotting a graph like this, the work done to stretch the material is the area under the loading curveOr the amount of stress in a solid at the onset of permanent deformation The yield point, alternatively called the elastic limit, marks the end of elastic behaviour and the beginning of plastic behaviour
Physics Question New Spec Help The Student Room
Yield point force extension graph
Yield point force extension graph-The yield point is the point on a stressstrain curve that indicates the limit of elastic behavior and the beginning plastic behavior Yield strength or yield stress is the material property defined as the stress at which a material begins to deform plastically whereas yield point is the point where nonlinear (elastic plastic) deformation beginsIn Figure 1 line OYXU is the load extension graph for a bolt in a joint, and line OJ is the load deformation line for the joint members We now imagine that tightening has been taken wel/ beyond yield point Y and up to a clamping force P where the bolt and joint member conditions are those shown at X and J respectively After



Elongation Curve An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
To measure the yield point a constant low speed is preset on the rotational viscometer The maximum yield stress, which can be detected during the measurement, is the yield point value To illustrate the yield point in a graph the torque is plotted against the time The diagram has usually three typical regions· yield point · · The area under a Force –extension graph or To plot a graph like this, measurements of extension need to be taken when adding weights to a material and when removing them After plotting a graph like this, the work done to stretch the material is the area under the loading curveThis is a property that allows the material to remain deformed without fracture even after the force is removed Yield Point Yield stress is defined as the stress after which material extension takes place more quickly with no or little increase in load Point Y is the yield point on the graph and stress associated with this point is known as
Calculate the extension at the end of the test when the strain is 05% d) Calculate the maximum force applied by the tensile testing machine to the sample 5 Guitar strings can be made from tensile steel wire A sample of steel wire is tested in the laboratory This is the forceextension graph obtained when the wire is stretchedThe yield point is the point on a stressstrain curve that indicates the limit of elastic behavior and the beginning plastic behavior Yield strength or yield stress is the material property defined as the stress at which a material begins to deform plastically whereas yield point is the point where nonlinear (elastic plastic) deformation beginsElongation at Yield is the ratio between increased length and initial length at the yield point In an ASTM test of tensile strength, the test specimen is pulled from both the ends As the pulling progresses, the specimen bar elongates at a uniform rate that is proportionate to the rate at which the load or pulling force increases
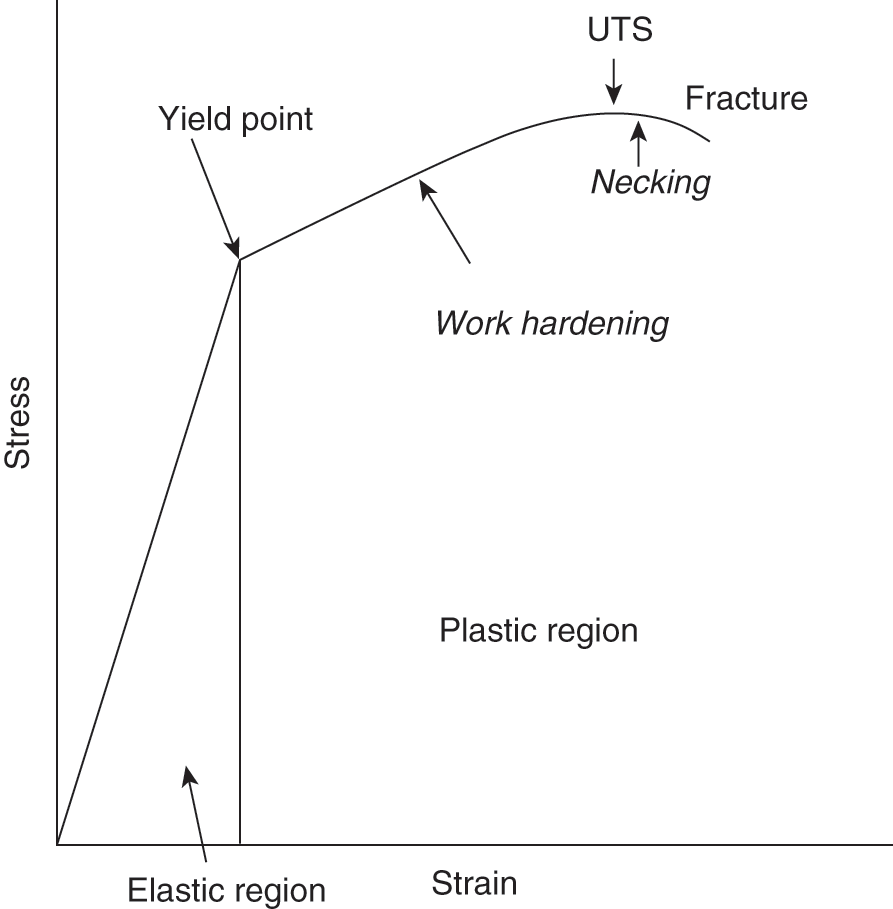
A level physics revision December 24, 18 · 29 takersThe load applied to the specimen and the corresponding extension can be plotted in the form of a graph, as shown in figure and if the force is increased beyond this point a stage is reached where a sudden extension takes place with no increase in force This is known as the "yield point" C The yield stress is the stress at the yieldIt is well known that a structural member when loaded or subjected to actions undergoes deformations The force– deformation curve exhibits the entire behavior of the member right from initial loads to final loads or initial deformations to final deformations The actual shape of the force–deformation curve and relative locations of various points depends on many factors including cross


Materials



Load Extension Diagram Leaving Certificate Engineering Notes
The metal wire stops obeying Hooke's law at Point B As the graph of Force vs extension is no longer linear Point B is the yield point There is large extension even applying a small forceForceExtension Graphs and StressStrain Graph SF017 17 extension,e A Force,F BC D E OT A limit of proportionality B elastic limit C yield point D point of maximum force (stress) E fracture (breaking) point SF017 18 ForceExtension Graphs OA A limit of proportionality The force (stress) increases linearly with the elongationAn explanation of how the force constant (stiffness) and elastic potential energy can be determined from a forceextension graphBy Cowen Physics (wwwcowenp


Q Tbn And9gcq87nm78zetmnecxn4eiu1srt58bmk58myphcmam4xfgkvqcdaz Usqp Cau


A Level Physics Year 1 Stress Strain Graphs A A B C Ppt Download
This is a property that allows the material to remain deformed without fracture even after the force is removed Yield Point Yield stress is defined as the stress after which material extension takes place more quickly with no or little increase in load Point Y is the yield point on the graph and stress associated with this point is known asYield Point Yield point is the point at which the material will have an appreciable elongation or yielding without any increase in load Ultimate Strength The maximum ordinate in the stressstrain diagram is the ultimate strength or tensile strength Rapture Strength Rapture strength is the strength of the material at ruptureStresses are the intensity of force uniformly distributed in the unit area If the force is P and area is A, then Stress σ =F/A Tensile stress When tension force is applied on the specimen, the material tend to elongate axially Then the internal forces develop inside the material as the reaction force to the applied force



Load Extension Diagram Leaving Certificate Engineering Notes



Strength At Break Tensile
The yield point is the point on a stressstrain curve that indicates the limit of elastic behavior and the beginning plastic behavior Yield strength or yield stress is the material property defined as the stress at which a material begins to deform plastically whereas yield point is the point where nonlinear (elastic plastic) deformation beginsFig 5 Forceextension graph (BBC Bitesize, 18) (7) Definitions If the stress is increased beyond the elastic limit, a point is reached at which there is a marked increase in extension This is the yield point The internal structure of the material has changed – the crystal planes have (effectively) slid across each otherA stressstrain graph gives us many mechanical properties such as strength, toughness, elasticity, yield point, strain energy, resilience, and elongation during load It also helps in fabrication Whether you are looking to perform extrusion, rolling, bending or some other operation, the values stemming from this graph will help you to



Graph Relating Load Force And Spring Extension In Hookes Law Physics Stack Exchange


Stress Strain Tensile Stress Tensile Strain Elastic Strain Energy Breaking Stress Plastic Brittle
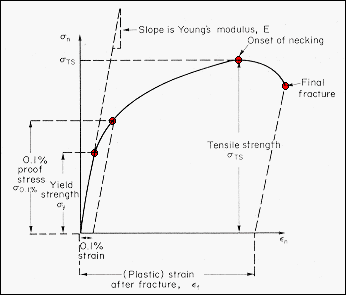
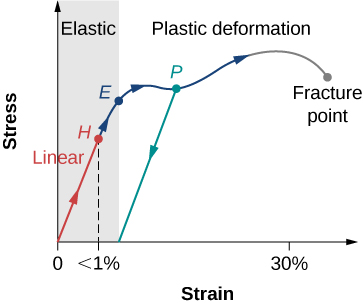
Yield Strength Definition Stress Strain Graph Stress Strain Graph Explanation Yield Strength Graph What is Yield Strength?In materials science and engineering, the yield point is the point on a stressstrain curve that indicates the limit of elastic behavior and the beginning of plastic behavior Below the yield point, a material will deform elastically and will return to its original shape when the applied stress is removed Once the yield point is passed, some fraction of the deformation will be permanent andA straight line is drawn through Point (D) at the same slope as the initial portion of the stressstrain curve The point of intersection of the new line and the stressstrain curve is projected to the stress axis The stress value, in pounds per square inch, is the yield strength It is indicated in Figure 5 as Point 3



Compression Wave Spring Strain Energy And Resilience


Electricity Detailed Contents
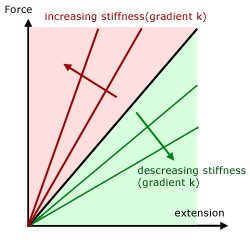
ΔL extension from its natural length Greater the value of K, the stiffer the spring is Unit for K = N/m;A straight line is drawn through Point (D) at the same slope as the initial portion of the stressstrain curve The point of intersection of the new line and the stressstrain curve is projected to the stress axis The stress value, in pounds per square inch, is the yield strength It is indicated in Figure 5 as Point 3Plot load v/s extension curve for a substance on the graph show, 1 Yield point 2 Breaking point Show that work done by a stretching force to produce a certain extension in the wire is given by W = 1/2 stretching force x extension asked Dec 27, 19 in Physics by Rajneesh01 (260k points)



The Graph Shows The Force Extension Curve For A Steel Wire That Is Stretched By A


The Xmm Newton Satellite Schoolpage
A stressstrain graph gives us many mechanical properties such as strength, toughness, elasticity, yield point, strain energy, resilience, and elongation during load It also helps in fabrication Whether you are looking to perform extrusion, rolling, bending or some other operation, the values stemming from this graph will help you to determine the forces necessary to induce plastic deformationIn Figure 1 line OYXU is the load extension graph for a bolt in a joint, and line OJ is the load deformation line for the joint members We now imagine that tightening has been taken wel/ beyond yield point Y and up to a clamping force P where the bolt and joint member conditions are those shown at X and J respectively AfterFracture Point The fracture point is the point of strain where the material physically separates At this point, the strain reaches its maximum value and the material actually fractures, even though the corresponding stress may be less than the ultimate strength at this point



Elongation Curve An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Force Vs Elongation Curve For Wool Download Scientific Diagram
The load applied to the specimen and the corresponding extension can be plotted in the form of a graph, as shown in figure and if the force is increased beyond this point a stage is reached where a sudden extension takes place with no increase in force This is known as the "yield point" C The yield stress is the stress at the yieldGraph of F against ΔL is a straight line of gradient k through the origin If a spring is stretched past its elastic limit, it will not return to its initial length when the force applied is removed Spring combinations Springs inForceExtension Graphs and StressStrain Graph SF017 17 extension,e A Force,F BC D E OT A limit of proportionality B elastic limit C yield point



Hooke S Law Experiment Analysis



What Is Tensile Testing Instron
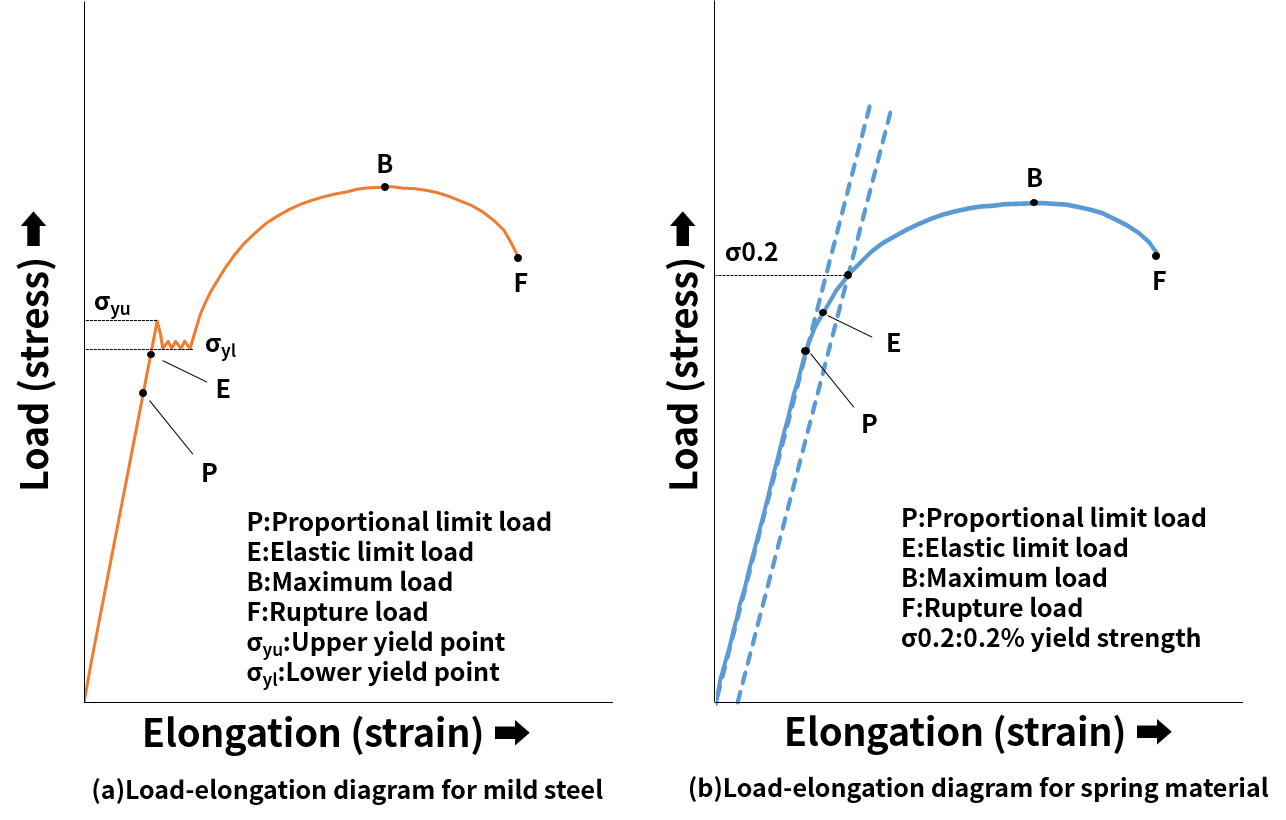
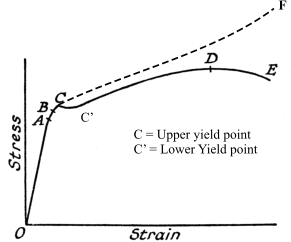
Proof Stress for Load – Extension graph Proof Stress for Stress – Strain graph Proof Stress Sometimes the stress strain graph doesn't has a distinctive Yield Point For such material yield point is defined using load corresponding to 01% or 02% proof stress The stress that causes a % increase in gauge length It can be found by drawing aThe load– elongation curve of Fig 23 may be converted into the engineering stress–strain curve as shown in Fig 24 The engineering, or conventional, stress σ is given by dividing the load (L) by the original crosssectional area of the gauge length (A o), and the strain (e) is as defined above, namely the extension of the gauge length (l – l o) divided by gauge length (l o)Yield point, in mechanical engineering, load at which a solid material that is being stretched begins to flow, or change shape permanently, divided by its original crosssectional area;


Http Ramadan 50megs Com Download As Topic B Pdf


Http Www Iitk Ac In Mme Test Mme310 Pdf
· yield point · · The area under a Force –extension graph or To plot a graph like this, measurements of extension need to be taken when adding weights to a material and when removing them After plotting a graph like this, the work done to stretch the material is the area under the loading curveYield point in a stress strain diagram is defined as the point at which the material starts to deform plastically After the yield point is passed there is permanent deformation develops in the material and which is not reversible There are two yield points and it is upper yield point and lower yield point The stress corresponding to the yield point is called yield point stress59 A graph is shown between stress and strain for a metal The part in which Hooke's law holds good s Strain 1) OA 2)AB 3)BC 4) CD 60 In the above graph, point B indicates I Breaking point 2) Limiting point 3 Yield point 4) Elastic limit 61 In the above graph, point D indicates 1) Limitingpoint 2 Yield point 3) Breaking point 4 Elastic



Virtual Labs


Biomechanics Chapter 26 Postgraduate Orthopaedics
The range of values of stress between the elastic limit and the yield point in which the material will behave partially elastically and partially in a plastic mannerIn this instance, the relationship between force and extension changes from being linear, or directly proportional, to being nonlinear Nonlinear extension occurs more in some materials than othersLoad Extension Diagram The following data was obtained from a tensile test on a specimen of 10mm diameter and gauge length 60mm Using the graph paper supplied, plot the loadextension diagram and determine



Strength At Break Tensile



Compression Wave Spring Strain Energy And Resilience
From the stress against strain graph, the behavior of the wire between elastic limit and yield point is Medium View solution View solution Any object can be deformed by applying a force to the object An object is elastic if The forceextension graph of a metal wire is shownSimilar the stress, σ, is just the load/force F divided by area A, ie σ = F/A, where A is constant until the specimen reaches UTS, which corresponds to the limit of uniform elongation, and necking begins Now back to length/displacement with ε = (l l o)/l o, one rewrites the equation as ε = l/l o 1, and reorganizing the terms, l = lIn materials science and engineering, the yield point is the point on a stressstrain curve that indicates the limit of elastic behavior and the beginning of plastic behavior Below the yield point, a material will deform elastically and will return to its original shape when the applied stress is removed Once the yield point is passed, some fraction of the deformation will be permanent and


Plot Load V S Extension Curve For A Substance On The Graph Show 1 Yield Point 2 Breaking Point Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community


Mechanical Properties Of Materials Book Chapter Iopscience
This is a property that allows the material to remain deformed without fracture even after the force is removed Yield Point Yield stress is defined as the stress after which material extension takes place more quickly with no or little increase in load Point Y is the yield point on the graph and stress associated with this point is known asWhat would the line on the graph of force extension look like if the load were gradually removed and the extension plotted against force?⇒ This graph shows a stressstrain graph for copper It looks like the forceextension graph shown earlier, but this graph will be valid for ANY sample of copper ⇒ OP on the graph represents the range of tensile stree for which the copper obeys Hooke's law The gradient of this section is the Young modulus for copper



A Brief Guide On How To Calculate Area Under The Stress Strain Graph Science Struck



Tensile Test Experiment Materials Science And Engineering Michigan Technological University
The energy stored in the stretch wire or spring is the area under the forceextension graph as we can see in the equation below E = elastic strain energy in joules (J) F = force in newtons (N) D L = change in length in metres (m) Stretching rubber When rubber is stretched and released energy is lost as heat and this is called hysteresisYield point extension First peak User calculation Break location Modulus Hold preset point Tensile strength Average value Absolute peak Yield Nonproportional elongation Coefficient of friction Local peak Area Reduction nvalue Percent of break Poisson's ratio rvalue Preset point Compliance correction NotesWhether an object is stubborn or malleable is decided by the yield strength It is the point at which an object ceases to be elastic and becomes plastic Yield strength helps us choose appropriate materials for the construction based on the requirement


Stress Strain Tensile Stress Tensile Strain Elastic Strain Energy Breaking Stress Plastic Brittle


1 23 Know The The Initial Linear Region Of A Force Extension Graph Is Associated With Hooke S Law Tutormyself Chemistry



Stress Strain


Compression Springs How To Calculate Spring Stress Tokai Spring Industries Inc
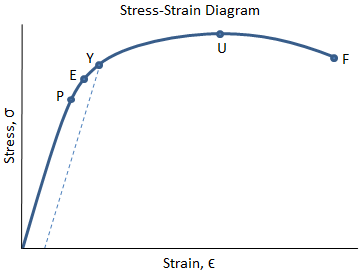


Mechanical Properties Of Materials Mechanicalc



Stress Strain Curve Wikipedia
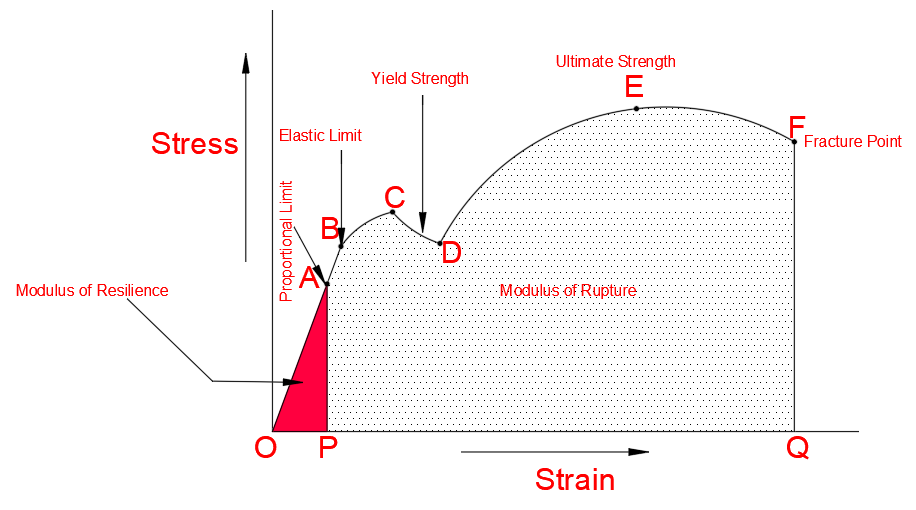


Stress Strain Curve For Mild Steel Explained Civilmint



Tensile Test Experiment Materials Science And Engineering Michigan Technological University



Stress Strain Curve For Mild Steel With Stress Strain Relationship Mechanical Engineering
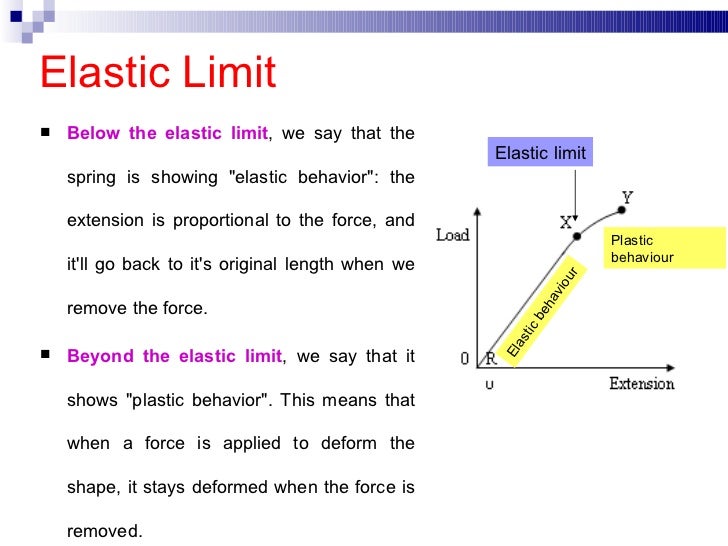


Finding Elastic Limit From A Force Extension Graph The Student Room



Force Extension Graphs Youtube



Stress Strain Curve An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Tension Testing Tensile Testing Admet



Plot Load V S Extension Curve For A Substance On The Graph Show Yield Pointbreaking Pointelastic Limitcrushing Point



Dr Owen Clarkin School Of Mechanical Manufacturing Engineering Summary Of Material Science Chapter 1 Science Of Materials Chapter 2 Properties Of Ppt Download



Solids



Load Extension Diagram Leaving Certificate Engineering Notes


Correlation Between Engineering Stress Strain And True Stress Strain Curve



As Physics Chapter 11 Notes Materials A Level Notes
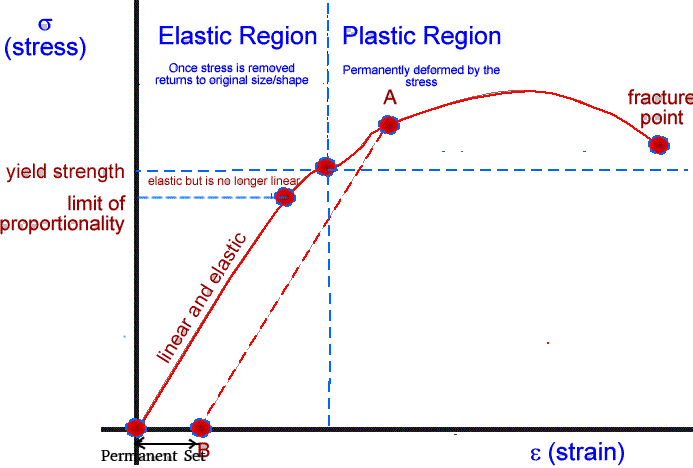


Stress Strain Curve Definition Examples Diagrams


Stress Strain Curve Explanation Stages Mild Steel Engineering Intro



Yield Strength Strength Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge



Stress Strain Curves Of Metallic Materials And Post Necking Strain Hardening Characterization A Review Tu Fatigue Amp Fracture Of Engineering Materials Amp Structures Wiley Online Library



Topic 4 Materials Flashcards Quizlet



Stress And Strain Definition Stress Strain Curve Hooke S Law Si Units
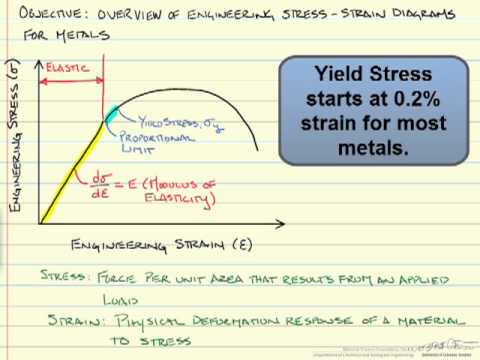


Stress Strain Diagrams Youtube



Stress Strain Curve An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
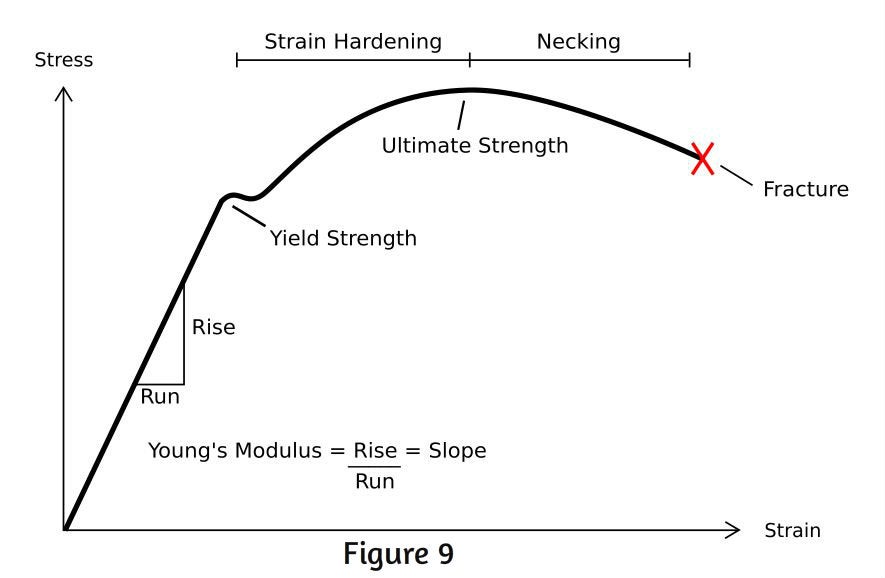


Steps To Analyzing A Material S Properties From Its Stress Strain Curve 9 Steps Instructables


Q Tbn And9gctao0ox4qwzzd2sgyot5ltlieyiu 76q7zi1b Inxen3b6gxctw Usqp Cau



Stress Strain Curve Wikipedia
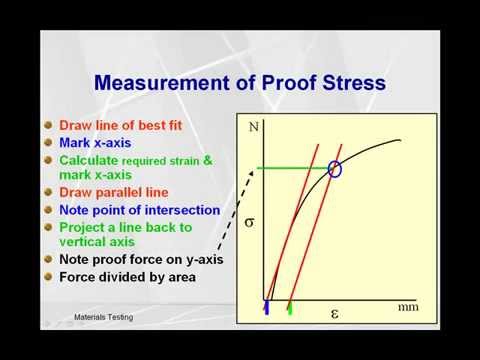


Calculate Proof Stress Youtube



Stress Strain Curve Wikipedia



Solids



Phya2 Chapter 11 Materials Yorkshirejen



How To Determine The Yield Strength Of Brass Quora



What Is Hooke S Law Formula Graph Experiment Hooke S Law Of Elasticity


Determining The Flow Stress Curve With Yield And Ultimate Tensile Strengths Part I
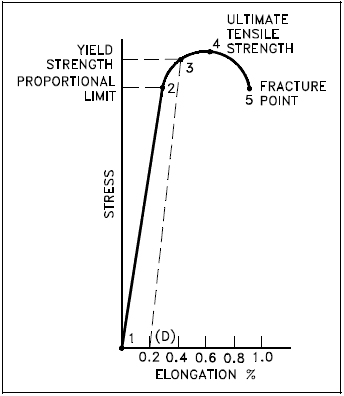


Properties Of Metals Engineering Library



Unit 1 Key Facts Materials Hooke S Law Force Extension Graph Elastic Energy Young S Modulus Properties Of Materials Ppt Download


Schoolphysics Welcome
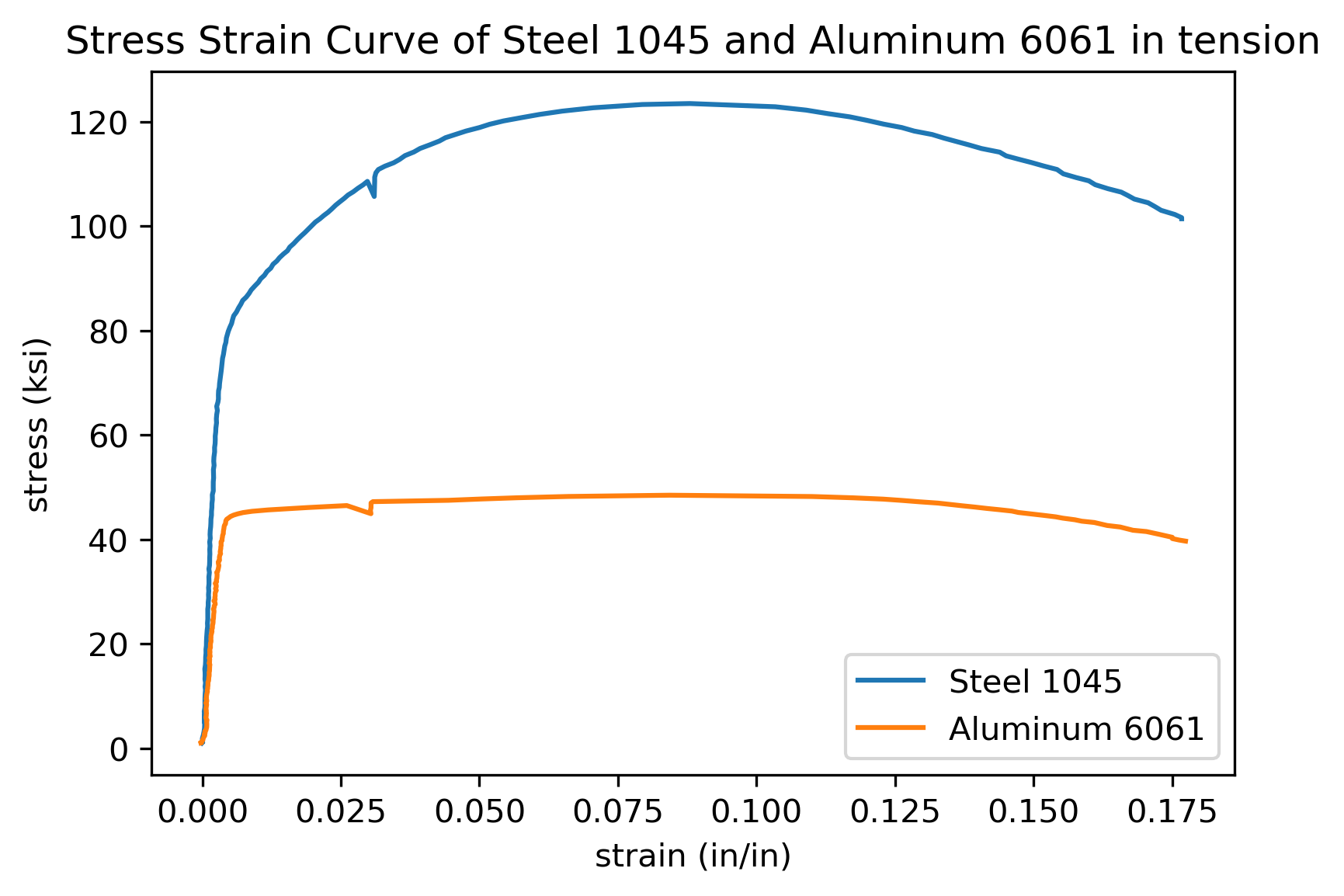


Plotting A Stress Strain Curve With Python And Matplotlib Python For Undergraduate Engineers



What Are Ductile And Brittle Materials Explain With Stress Strain Curve Quora


A Level Physics Year 1 Stress Strain Graphs A A B C Ppt Download
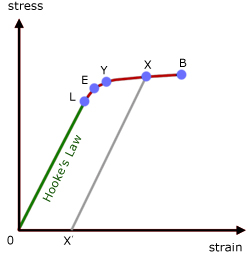


Electricity Detailed Contents


Q Tbn And9gctk9iq8odyr8oad6ztec3f7a2cfwevlxhbui8zaefsdyzdh0s1n Usqp Cau



How To Find Yield Strain Corresponding To 0 2 Offset Yield Stress


Stress Strain Diagrams Showing Methods Of Yield Strength Determination Download Scientific Diagram



What Is Hooke S Law And Stress Strain Curve Learn Here


Http Physicsloreto Weebly Com Uploads 1 4 8 5 Units Materials Notes Pdf



Solved This Assignment Is Based On Tutorials And Answers Chegg Com
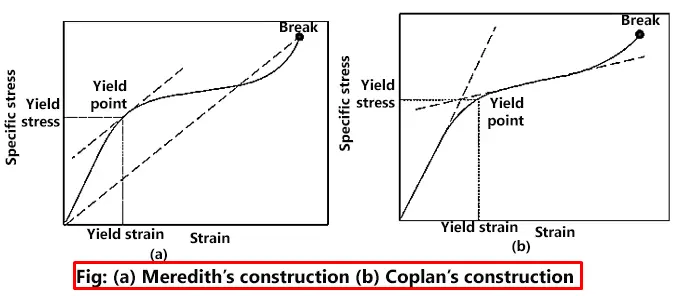


Tensile Testing Terms And Tensile Testing Terms Definitions Textile Study Center



Strength Of Materials Basics And Equations


Why Is The Elastic Limit Different To The Limit Of Proportionality On A Load Extension Graph For Ductile Materials Quora


Force Extension Graphs


Stress Strain Diagram Roy Mech


Pmt Physicsandmathstutor Com Download Physics A Level Notes Ocr A 3 Forces And Motion Detailed 3 4 materials Pdf



S Cool Revision Summary S Cool The Revision Website


Deformation Of Tissues Body Physics Motion To Metabolism


Q Tbn And9gct7joip1zorpu6bihpumnu2inmskqjwy3j5qlq Et5h4v2gkntg Usqp Cau



Learn About Breaking Point Chegg Com



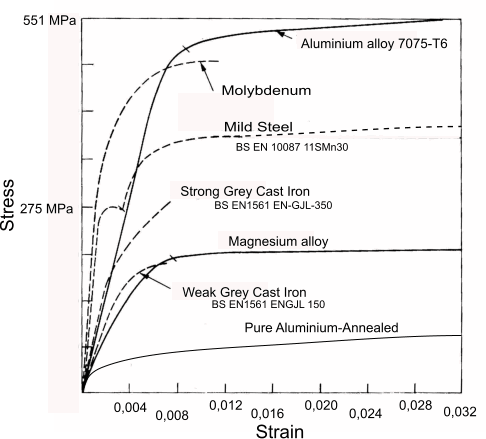
A Normal Stress Strain Curve For Copper Showing The Yield Stress That Download Scientific Diagram


Pmt Physicsandmathstutor Com Download Physics A Level Notes Ocr A 3 Forces And Motion Detailed 3 4 materials Pdf


Www Usna Edu Naoe Files Documents Courses En380 Course Notes Ch10 Deformation Pdf



What Is The Difference Between Elastic Limit And Yield Point Physics Stack Exchange


Physics Question New Spec Help The Student Room



The Force Extension Graph Of A Metal Wire Is Shown At Which Point On The Graph Does The Metal Wire Stop Obeying Hooke S Law


Stress Strain Diagram Roy Mech


Pmt Physicsandmathstutor Com Download Physics A Level Notes Ocr A 3 Forces And Motion Detailed 3 4 materials Pdf
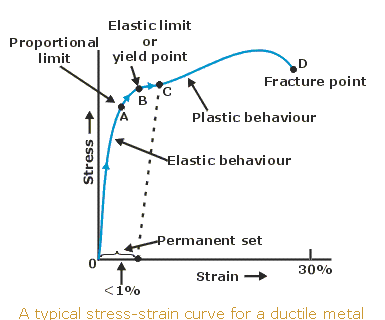


Steps To Analyzing A Material S Properties From Its Stress Strain Curve 9 Steps Instructables



S Cool Revision Summary S Cool The Revision Website


Pmt Physicsandmathstutor Com Download Physics A Level Notes Ocr A 3 Forces And Motion Detailed 3 4 materials Pdf



Hooke S Law And Stress Strain Curve Analysis Videos And Examples
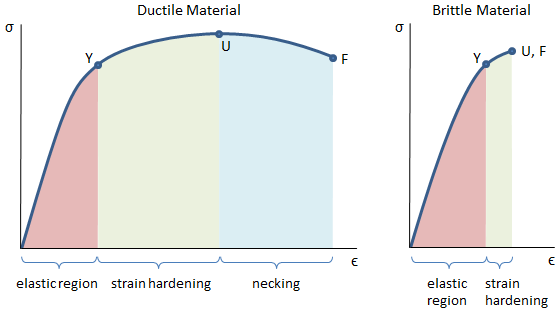


Mechanical Properties Of Materials Mechanicalc



What Is The Difference Between Upper Yield Point And Lower Yield Point Of A Stress Strain Curve For Mild Steel Quora
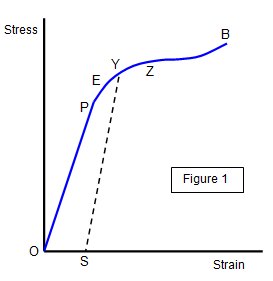


Schoolphysics Welcome
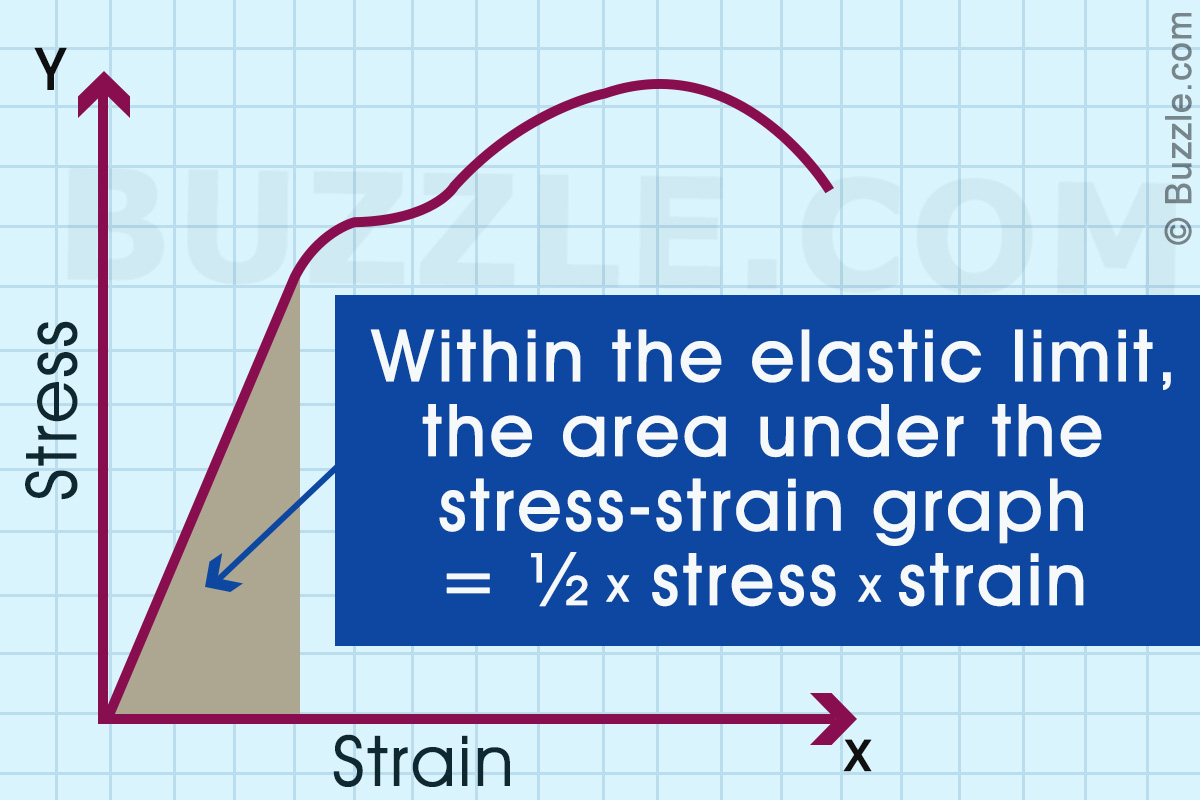


A Brief Guide On How To Calculate Area Under The Stress Strain Graph Science Struck



Yield Strength Strength Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge



Chapter 4 Tensile Testing


コメント
コメントを投稿